Country / Territory
Related contacts
Related offices
Related contacts
Related insights
Related offices
Related contacts
Related insights
Related offices
By: Shoaib Khaleeli
In the final part of this blog series on Emiratisation, Immigration Manager Shoaib Khaleeli explores the impact of Emiratisation-related non-compliance and how employers can prioritise preparing to remain compliant.
Impacts of non-compliance
In the event companies have not been able to comply to the rules and requirements, as a first step they may be notified by the relevant authority through an email or other communication channel. Further notices will be sent on the 3rd, 10th and 17th days after the due date.
Some companies have already started receiving these notices. It is important to proactively be aware of your Emiratisation Ratio in order to not fall into non-compliance, and waiting for the notification is not a recommended course of action.
Primarily, the authorities are using a combination of financial contribution (penalty) and administrative restrictions to drive compliance. For those companies not hiring appropriate levels of UAE Nationals, there is a specific financial contribution required to the authorities.
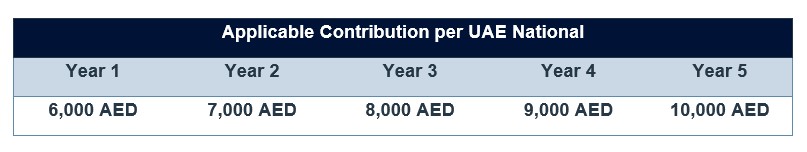
In the first year, the applicable contribution amount is 6,000 AED per month. This applicable contribution amount is set to increase with every year by 1000 AED, thus, by the end of year 5, the total applicable contribution per UAE national would be 10,000 AED a month.
As mentioned in a previous instalment of this series, from 2023 onward, the Emiratisation Ratio will be calculated monthly. Therefore, for each month that the company does not meet the Emiratisation requirement, a monthly contribution of 6,000 AED per UAE national not hired will be calculated.
The contribution formula to calculate the total contribution owed to the MOHRE authorities can be described as:
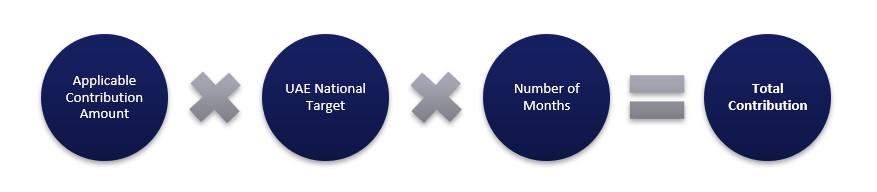
Using an example of a company with 50 skilled employees, the company should have hired one Emirati in the first year. Therefore, the total contribution in the first year would be calculated as:
Applicable Contribution Amount (6,000 AED) X Target Number of UAE nationals (1) X Number of Months (12) = AED 72,000.
Other than significant financial penalties, the MOHRE can also leverage administrative penalties against non-compliant companies. These administrative penalties may include:
- The suspension of the companies’ MOHRE system from the ability to renew or hire new employee (a system block) on the day after the contribution due date;
- The suspension of any other associated companies’ (under same group/ownership) MOHRE system from the ability to renew or hire new employee (a system block) two months after the contribution due date; and/or
- If companies did not meet the requirements for a period of two years, the authorities will downgrade the classification of the companies' registration categories to the lowest, resulting in hiring government fees.
The authorities also can administer further penalties to institutions of up to 20,000 AED per person in the instance a company submitted incorrect documents to the authorities during the registration process or illegitimately benefited from the Emiratisation.
Considerations for employers
Prioritising compliance with Emiratisation requirements has never been more important. The significant financial penalties and further administrative restrictions have the potential to cripple work authorisation and renewal processes, which can lead to restrictions in immigration status for affected individuals as well as permanently devalue a company’s establishment category.
With this in mind, proactive engagement by employers is paramount. Some action items are:
- Understand your Emiratisation Rate;
- Prioritise hiring Emiratis to skilled positions, and make this a key component of long-term growth strategy;
- Set up an Emiratisation programme that includes engagement, planning and constant monitoring; and
- Leverage the multiple benefits being provided by Nafis for hiring Emiratis
Designing a thoughtfully-approached and efficient Emiratisation programme can be a challenge for some, especially with new regulations and the associated administrative practises being constantly developed. As the authorities exercise stricter practices related to this topic, navigating Emiratisation well can turn out to be a competitive advantage for those who get it right.
Need to know more?
Please refer to the first blog in the series for information on the new Emiratisation requirements and the second blog in the series for specifics of the Emiratisation calculation.
For any further information, please contact Immigration Manager Shoaib Khaleeli at [email protected]. This blog was published on 18 January 2023, and due to the circumstances, there are frequent changes.
To keep up to date with all the latest updates on global immigration, please subscribe to our alerts and follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook and Instagram.
Country / Territory
Related contacts
Related offices
Related contacts
Related insights
Related offices
Related contacts
Related insights
Related offices
Explore more at Fragomen

Video
Partner Diana Quintas outlines key early career visa pathways and practical considerations for employers and graduates navigating entry-level immigration options.

Fragomen news
The Montreal office has added Partner Julie Lessard and Counsel Elsa Agostinho and Sophia Khanzadian to strengthen its immigration services.

Blog post
Destination Services Director Christine Sperr examines how housing market reforms, rent stabilization measures and cost-of-living dynamics in Saudi Arabia are influencing workforce mobility, compensation planning and long-term settlement strategies under Vision 2030.

Blog post
Manager Dr Adela Schmidt and Senior Associate Isabel Schnitzler analyse the European Commission’s infringement proceedings against Germany concerning its Vander Elst visa requirements for third-country nationals providing short-term cross-border services and explain why current compliance obligations remain unchanged.

Blog post
Latin America & the Caribbean Managing Partner Leonor Echeverria, Senior Associates Sarah Blackmore and Sonya Cole and Senior Regional Knowledge Manager Laura Weingort examine renewed energy interest in Venezuela and outline key immigration pathways, procedural constraints and strategic considerations for compliant talent deployment.

Media mentions
Senior Manager Andreia Ghimis highlights how the EU’s new migration strategy could create opportunities for employers while increasing compliance requirements.

Awards
Partner Julia Onslow-Cole is recognised in the Spears 500 guide to leading private client advisers, reflecting her experience advising high-net-worth individuals, families and global businesses on complex UK and European immigration and mobility strategies.

Media mentions
Partner Abeer Al Husseini discusses increased scrutiny of Saudi business visas in AGBI, highlighting stricter review of short-term entry used for operational work and the implications for regional employers.

Awards
Australia and New Zealand Managing Partner Teresa Liu, Partner Charles Johanes, Practice Leaders Hedvika and Leader Ben Lear and Senior Associate Hannah Scanlan are recognized in the 2026 edition of Doyle’s Guide as leading immigration practitioners in Australia.
Awards
Fragomen is ranked Band 1 for Immigration: Business in the Chambers Global 2026 Guide, marking two decades of recognition since 2006. The firm is also the only firm ranked Band 1 in the Global: Multi-Jurisdictional Immigration category and receives additional individual recognitions in the USA: Business Immigration rankings.

Media mentions
Partner Rick Lamanna provides insight to Buffalo Toronto Public Media on potential IRCC processing challenges as Canada prepares for increased visa demand ahead of the 2026 FIFA World Cup.

Video
Partner Diana Quintas outlines key early career visa pathways and practical considerations for employers and graduates navigating entry-level immigration options.

Fragomen news
The Montreal office has added Partner Julie Lessard and Counsel Elsa Agostinho and Sophia Khanzadian to strengthen its immigration services.

Blog post
Destination Services Director Christine Sperr examines how housing market reforms, rent stabilization measures and cost-of-living dynamics in Saudi Arabia are influencing workforce mobility, compensation planning and long-term settlement strategies under Vision 2030.

Blog post
Manager Dr Adela Schmidt and Senior Associate Isabel Schnitzler analyse the European Commission’s infringement proceedings against Germany concerning its Vander Elst visa requirements for third-country nationals providing short-term cross-border services and explain why current compliance obligations remain unchanged.

Blog post
Latin America & the Caribbean Managing Partner Leonor Echeverria, Senior Associates Sarah Blackmore and Sonya Cole and Senior Regional Knowledge Manager Laura Weingort examine renewed energy interest in Venezuela and outline key immigration pathways, procedural constraints and strategic considerations for compliant talent deployment.

Media mentions
Senior Manager Andreia Ghimis highlights how the EU’s new migration strategy could create opportunities for employers while increasing compliance requirements.

Awards
Partner Julia Onslow-Cole is recognised in the Spears 500 guide to leading private client advisers, reflecting her experience advising high-net-worth individuals, families and global businesses on complex UK and European immigration and mobility strategies.

Media mentions
Partner Abeer Al Husseini discusses increased scrutiny of Saudi business visas in AGBI, highlighting stricter review of short-term entry used for operational work and the implications for regional employers.

Awards
Australia and New Zealand Managing Partner Teresa Liu, Partner Charles Johanes, Practice Leaders Hedvika and Leader Ben Lear and Senior Associate Hannah Scanlan are recognized in the 2026 edition of Doyle’s Guide as leading immigration practitioners in Australia.

Awards
Fragomen is ranked Band 1 for Immigration: Business in the Chambers Global 2026 Guide, marking two decades of recognition since 2006. The firm is also the only firm ranked Band 1 in the Global: Multi-Jurisdictional Immigration category and receives additional individual recognitions in the USA: Business Immigration rankings.

Media mentions
Partner Rick Lamanna provides insight to Buffalo Toronto Public Media on potential IRCC processing challenges as Canada prepares for increased visa demand ahead of the 2026 FIFA World Cup.



